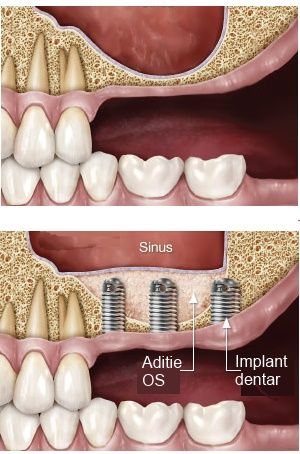
The maxillary sinus is a cavity inside the jawbone, filled with air and communicating with the nasal cavity and the other sinuses (frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid). This cavity is often in direct proximity to the roots of the molars and premolars. When these teeth are extracted, the alveolar bone in which they have been implanted is reabsorbed by a normal physiological process, due partly to the lack of stimulation of the bone (through the roots of the teeth, the bone receives physiological forces which stimulate its trophicity) and partly to the pressure exerted by the air in the sinus cavities.
Due to this resorption often the amount of bone is insufficient for the correct insertion of a dental implant. In order to correctly assess the amount of bone, basic investigations such as panoramic X-rays which give an overview and CT scans for a more detailed picture of bone structure and density are necessary.
The sinus lift procedure involves lifting the mucosa lining the sinus and inserting artificial or natural bone to increase the bone supply for the dental implant by a few millimetres.
After sinus lift surgery without dental implant insertion, a minimum period of 6-9 months is expected before the dental implant can be inserted.
 RO
RO  EN
EN 