Maxillofacial surgery
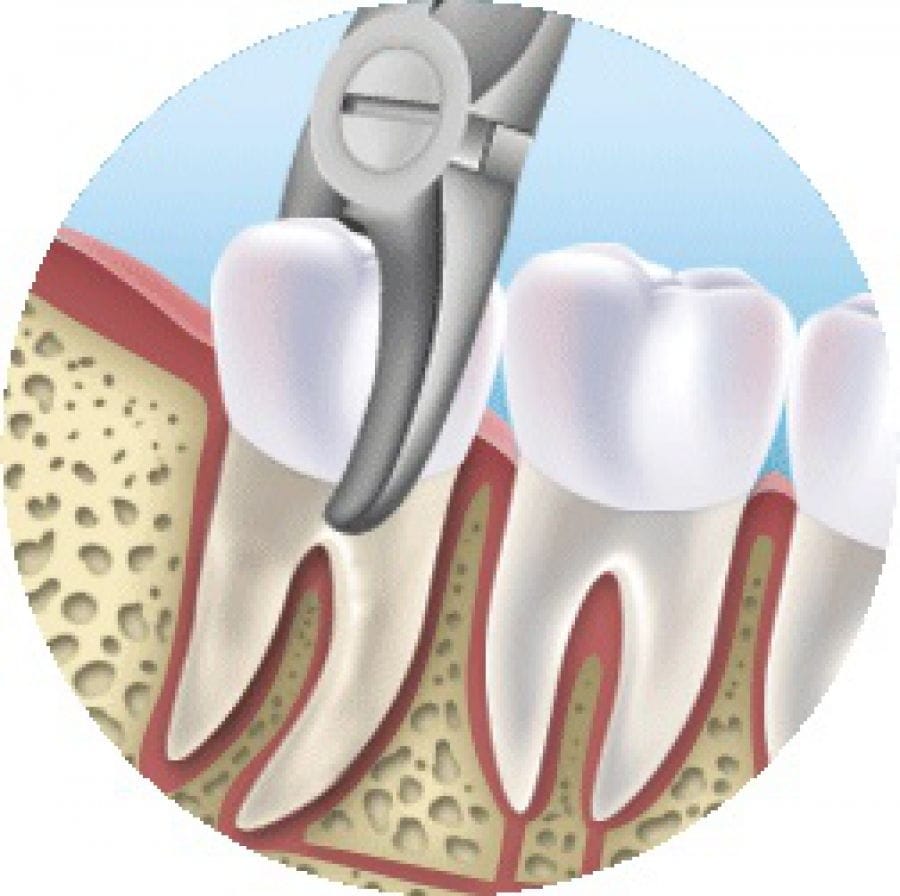
The most common surgical procedure in dentistry is tooth extraction. When a tooth is destroyed and can no longer be restored or there are complications at the tooth root - periapical complications - then the tooth must be extracted. The extracted tooth can be replaced with a dental implant or a dental bridge.

When the jawbones do not meet correctly, resulting in malocclusion, orthognathic surgery is needed. Orthognathic surgery repositions the facial bones in an optimal balance and improves the physiognomy. The aim of orthognathic surgery is to correct the facial structure, reconstructing the correct occlusion and giving optimal functionality to the teeth.

Sinus-lifting is a surgical procedure aimed at improving the conditions for the application of dental implants to bone atrophy of the upper jaw.

The temporomandibular joint connects the lower jaw (mandible) to the temporal bone of the skull and is attached to each side of the face, just below the ear. This joint is flexible allowing the jaw to move up and down on either side and facilitating processes such as speaking, chewing and even yawning. Muscles attached around the temporomandibular joint control the position and movement of the jaw.
 RO
RO  EN
EN 